Copper is well-poised to take centre stage in terms of future development and innovation in a rapidly expanding, technologically driven, and sustainability-seeking modern society.
One way to think about sustainability is the decarbonization of the global economy or an increase in the copper intensity of GDP.
Decarbonization of the global economy can be broken down into three factors:
- Reduction in energy demand
- Improved energy efficiency
- Reduction in CO2 per unit of energy produced
The first factor would require 7.5 billion people on earth to work together to reduce their energy footprint. However, the second and third factors have been steadily improving thanks to technology and one raw material – copper.
Copper’s ‘Sustainable’ Characteristics
 Copper has inherent properties not found in other major elements in the periodic table, namely unmatched thermal and electrical conductivity, ductility, malleability, corrosion resistance, greater safety than other conductive metals and recyclability.
Copper has inherent properties not found in other major elements in the periodic table, namely unmatched thermal and electrical conductivity, ductility, malleability, corrosion resistance, greater safety than other conductive metals and recyclability.
Copper has been in use for more than 10,000 years due to its versatile qualities and new innovative applications for the metal are still being developed (i.e. semi-conductor copper chip and batteries to store renewable energy).
Creative Sustainability
Copper’s role in sustainable development initiatives cannot be overlooked.
Global demand for renewable energy has reached unparalleled status. In the first half of 2019 renewables produced more energy than fossil fuels in Europe, according to EnAppSys. Power from wind and solar require 3 to 15 times as much copper per unit of output as fossil fuels.
Alongside the world’s growing commitment to efforts in sustainability and efficiencies in multiple industries, copper is leading the charge in finding new ways to do old things. The rise in electric vehicles, can in part, be attributed to the significant energy efficiencies generated with copper. Copper’s lower-cost and energy ‘space-saving’ abilities in the motor manufacturing process, ultimately, extend to the entire lifecycle of the motor itself.
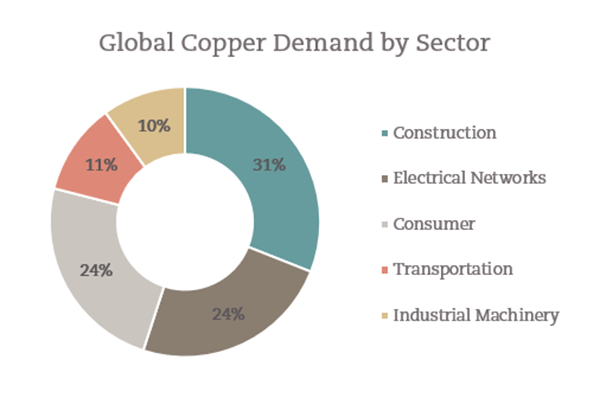
Economic growth and urbanization in developing countries have prompted rapid demand for the metal in terms of buildings electrical distribution and telecommunications infrastructure as well as modern appliances (i.e. refrigeration units and air conditioners). As urbanization progresses the energy output in these areas will unquestionably skyrocket. About 40 per cent of the world’s primary energy consumption stems from buildings. Copper is seen as the antidote to that consumption - making buildings more energy-efficient.
The stringent requirements for 5G connection and technologies are expected to rely heavily upon the interconnected intensive 5G fibre-optic backbone (copper a key component) necessary to seamlessly stream band-with intensive applications (i.e. 4K video, VR & AR, Robotics and Automation, Autonomous Vehicles, med-tech etc.) Regardless of the connection, energy supply and wireless technology employed, copper is an important and increasingly utilized input.
Macro Reserve(ation)s
Copper, traditionally known as a gauge on the health of the global economy, has now been in an overall bearish standing for 2019. Mid-2019 Copper was at the most bearish level on record according to the CFTC data going back to 1989, surpassing the previous bearish record in June of 2006 – typically bullish and bearish indicators at such an extreme level is a contrarian indicator.
Despite reduced forecasts of global growth due to trade wars, Brexit, geopolitics and other market uncertainties, Sandstone is taking a more optimistic view of copper’s future. We view copper as a versatile commodity that, despite perhaps a few market hiccups to come over the short-term, will ultimately continue to present its steady-demand status, worldwide.
Bottom Line
Macro uncertainties notwithstanding, copper is a principal contributor to global development and a key input into Sandstone’s investment themes of Disruptive Technology, 5G, and Infrastructure Push to name a few.
Sandstone has copper exposure in portfolios through Lundin Mining a Canadian copper mining company with strong cash-flow, a flexible balance sheet, company-specific catalysts, a sustainable dividend (recently increased 33%) and which was purchased at an attractive relative valuation.
As the world seeks new and sustainable ways to innovate on platforms from power generation and electricity to infrastructure and technology—copper will be a significant input.